WebSphere MQ messages are made up of two parts:
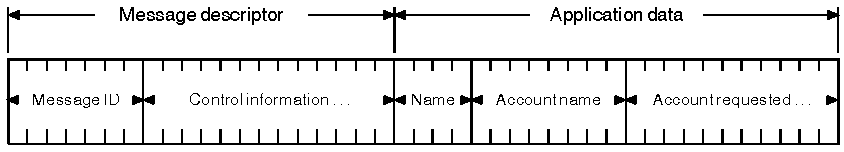
Figure 2 represents a message and shows how it is logically divided into message data and application data.
Figure 2. Representation of a message

The application data carried in a WebSphere MQ message is not changed by a queue manager unless data conversion is carried out on it. Also, WebSphere MQ does not put any restrictions on the content of this data. The length of the data in each message cannot exceed the value of the MaxMsgLength attribute of both the queue and queue manager.
In WebSphere MQ for AIX, WebSphere MQ for iSeries, WebSphere MQ for HP-UX, WebSphere MQ for Linux for Intel and Linux for zSeries, MQSeries for OS/2 Warp, WebSphere MQ for Solaris, MQSeries for Compaq Tru64 UNIX, and WebSphere MQ for Windows, the MaxMsgLength defaults to 100 MB (104 857 600 bytes).
In WebSphere MQ for z/OS, the MaxMsgLength attribute of the queue manager is fixed at 100 MB and the MaxMsgLength attribute of the queue defaults to 4 MB (4 194 304 bytes) which you can change up to a maximum of 100 MB if required. However, the limit is 63 KB when using shared queues accessed by queue managers in a queue-sharing group.
In MQSeries for AT&T GIS UNIX, MQSeries for Compaq OpenVMS Alpha, MQSeries for SINIX and DC/OSx, MQSeries for Compaq NonStop Kernel, MQSeries for VSE/ESA and the MaxMsgLength defaults to 4 MB.
However, you should make your messages slightly shorter than the value of the MaxMsgLength attribute in some circumstances. See The data in your message for more information.
You create a message when you use the MQPUT or MQPUT1 MQI calls. As input to these calls, you supply the control information (such as the priority of the message, and the name of a reply queue) and your data, and the call then puts the message on a queue. See WebSphere MQ Application Programming Reference for more information on these calls.
This chapter introduces WebSphere MQ messages, under these headings: